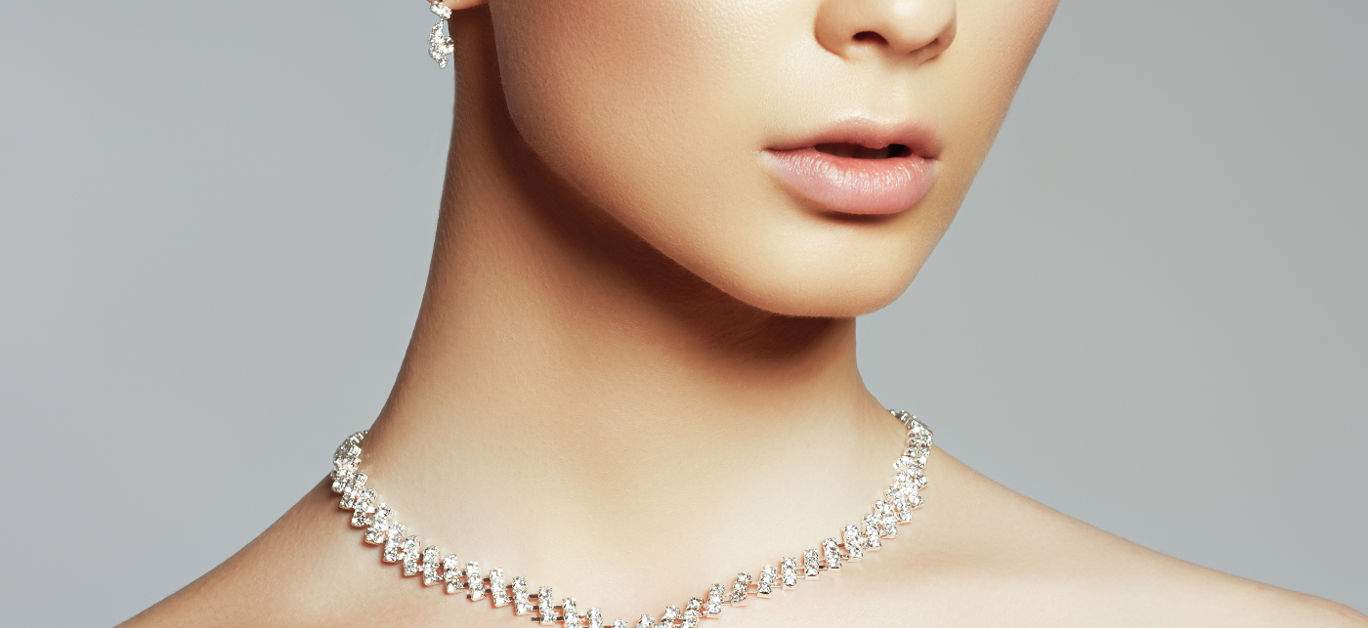
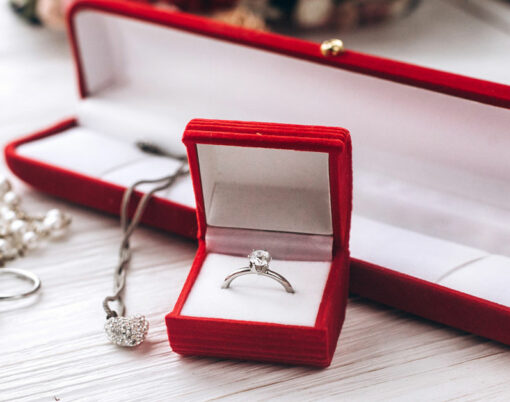
Everyone knows that diamonds are a girl’s best friend – but where once it was a statement that referred only to the naturally mined kind, in 2024, the lab-grown diamond is proving just as popular.
In recent years, we’ve seen a remarkable shift in the diamond industry, with the rise of lab-grown diamonds heralding a new era for these spectacular, sparkling jewels.
Revolutionising the traditional diamond market by offering an ethical, sustainable, and more cost-effective alternative, their appeal has not gone unnoticed by consumers who are becoming increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impact of their purchases,
In fact, far from it, as lab grown diamonds have seen a dramatic surge in sales over recent years. Could we be about to turn our backs on the original gemstones for good in favour of this modern alternative? Here, we take a look at why the lab-grown diamond is fast becoming the flavour of our times for jewellery enthusiasts, collectors and investors across the globe alike, and explore the implications of this burgeoning trend on the future of the diamond industry.

What are lab grown diamonds?
Lab-grown diamonds, also referred to as lab-created diamonds, synthetic diamonds, engineered diamonds and cultured diamonds, are produced in meticulously controlled laboratory settings utilising advanced technological methods that replicate the natural conditions in which diamonds form in the mantle beneath the Earth’s crust. These shiny synthetic stones are composed of genuine carbon atoms organised in the distinct crystal structure characteristic of diamonds, and because they are composed from the same material as natural diamonds, they also demonstrate identical optical and chemical properties.
Lab-grown diamond engagement rings and other types of lab-grown diamond jewellery are therefore becoming ever more popular – not just because they allow buyers to maximise their budgets, but more importantly because they come without the controversial implications of traditional diamond mining attached.
How are lab grown diamonds made?
Lab-grown diamonds are made using two main processes: chemical vapour deposition (CVD) and high pressure high temperature (HPHT). Scientists have devised these methods to replicate the natural diamond growth process in a laboratory setting, and have made it possible to produce authentic lab diamonds that are virtually indistinguishable from naturally occurring diamonds.
The HPHT method replicates the intense conditions deep within the Earth, where natural diamonds are formed. To create lab diamonds using HPHT, a large machine is supplied with carbon material, which it then crushes under pressures exceeding 870,000 pounds per square inch at temperatures ranging from 1300 to 1600 degrees celsius.

In chemical vapour deposition (CVD), a small vacuum chamber containing a seed diamond is filled with heated hydrogen and carbon-containing gasses. As the gas molecules break down at a specific temperature, layers of crystalised carbon start forming around the seed, gradually growing a larger diamond. Some lab diamonds produced through CVD may undergo additional pressure and heat treatment after their growth.
It’s impossible to tell natural diamonds and lab diamonds grown using the HPHT or CVD methods apart with the naked eye, and only scientists can discern the differences by examining identifying markers caused by the growth conditions.
Lab grown diamonds vs. natural diamonds
Without specialised equipment, natural and lab-grown diamonds look identical, sharing the same physical, chemical, and optical traits, including their sparkle, fire, and scintillation. Although lab-created diamonds may contain different trace elements compared to natural ones, these differences don’t affect the diamond’s appearance.
Why lab-grown diamonds have got the edge
According to Hatton Garden jewellers Mouza, lab-grown diamonds offer several advantages over mined diamonds besides the obvious plus points of being physically indistinguishable, responsibly sourced, and more affordable.
Lab-grown diamonds typically exhibit fewer imperfections compared to mined ones, making it easier to find a flawless stone, which appeals to many buyers and allows them to opt for a truly perfect diamond for an engagement ring, diamond necklace or other show-stopping piece of jewellery.

Lab-grown diamonds often come at a lower cost than mined diamonds of similar quality. For those for whom money is no object, price is often neither here nor there – but when you consider that you could actually lay your hands on a more perfect stone for a lower cost, even the world’s wealthiest individuals can’t ignore this advantage.
A diamond with a unique colour makes for a truly show-stopping piece of jewellery and exudes a sense of exclusivity – something that will invariably appeal to the luxury lover. Laboratories can create rare diamond hues that are seldom found in nature, making them more accessible, but you can still have them made into unique and bespoke items of jewellery that no-one else has – making it easier than ever before to bring your vision for that dream ring, necklace or pair of earrings to life.
Another key benefit of lab-grown diamonds is that they can always be traced back to reputable sources, ensuring fair treatment of workers and communities.
The HPHT and CVD methods used for lab-grown diamonds also facilitate meeting demand sustainably without compromising quality or resorting to harmful practices – so it’s easy to see why a growing number of diamond lovers are opting for them instead.